ROSA® Knee with OptimiZe™: Robotic Knee Arthoplasty
OptimiZe to Personalize™
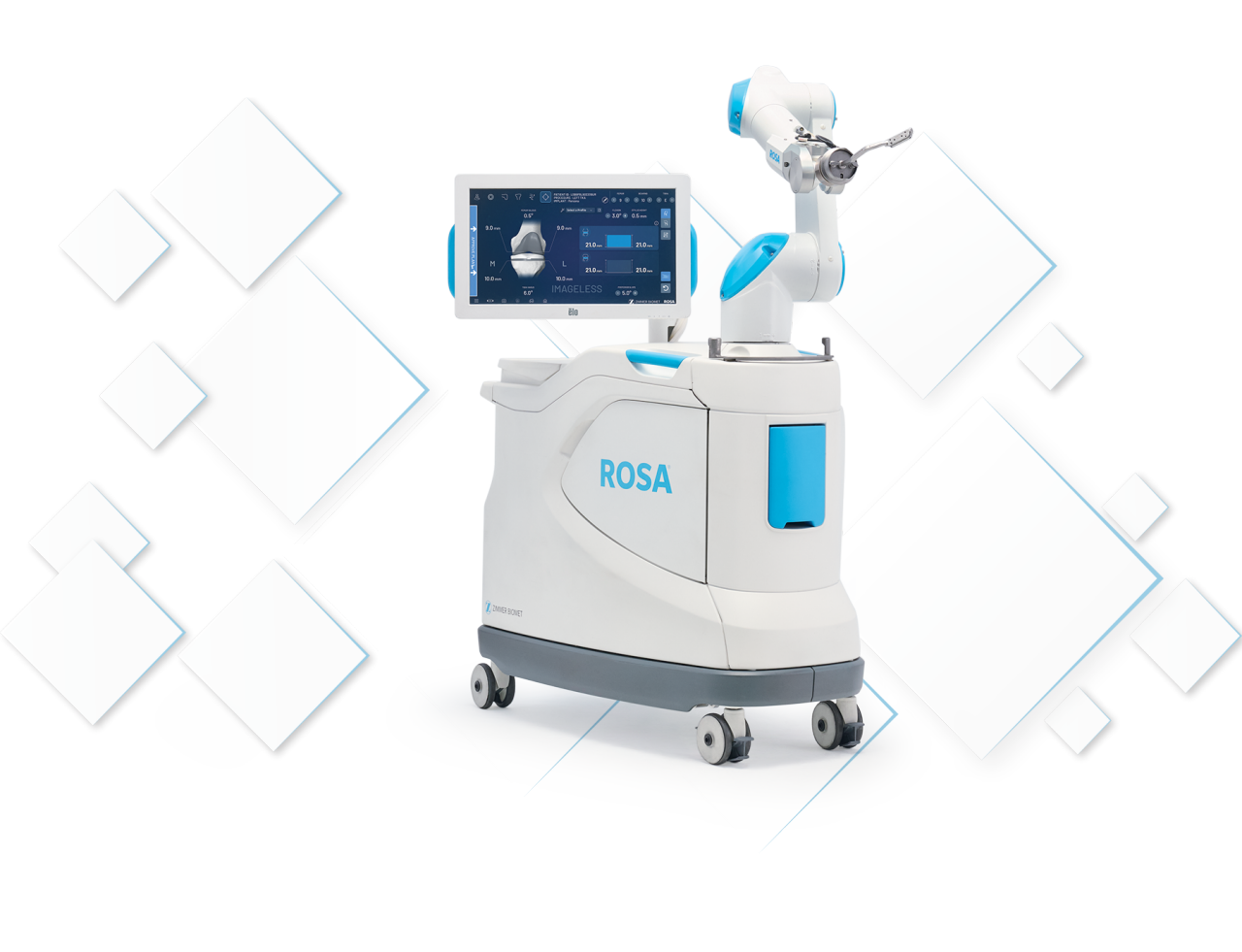

ROSA® Knee with OptimiZe™
Provides intelligent, personalized surgical plans and enhanced landmarking that reduces surgical variability,1 driving surgeon confidence in accurate and reproducible robotic TKA outcomes.2
Features
ROSA Knee with OptimiZe boasts unique features to optimize surgical procedure accuracy and efficiency.
Benefits
Surgeon-Centered
You’re in the Driver’s Seat
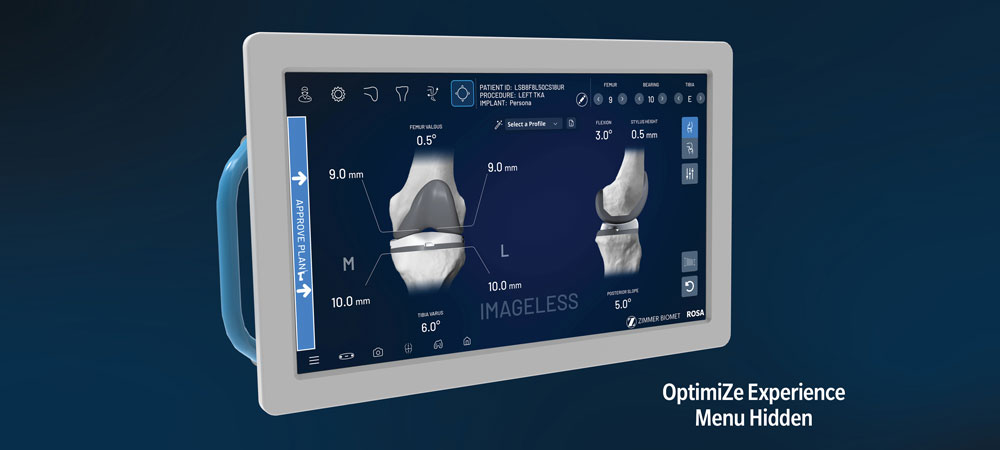
Allows you to maintain your current surgical workflow, while enabling you to OptimiZe your robotic experience through customized surgeon profiles, personalized, anatomically accurate implants3,4 and optimized instrumentation.
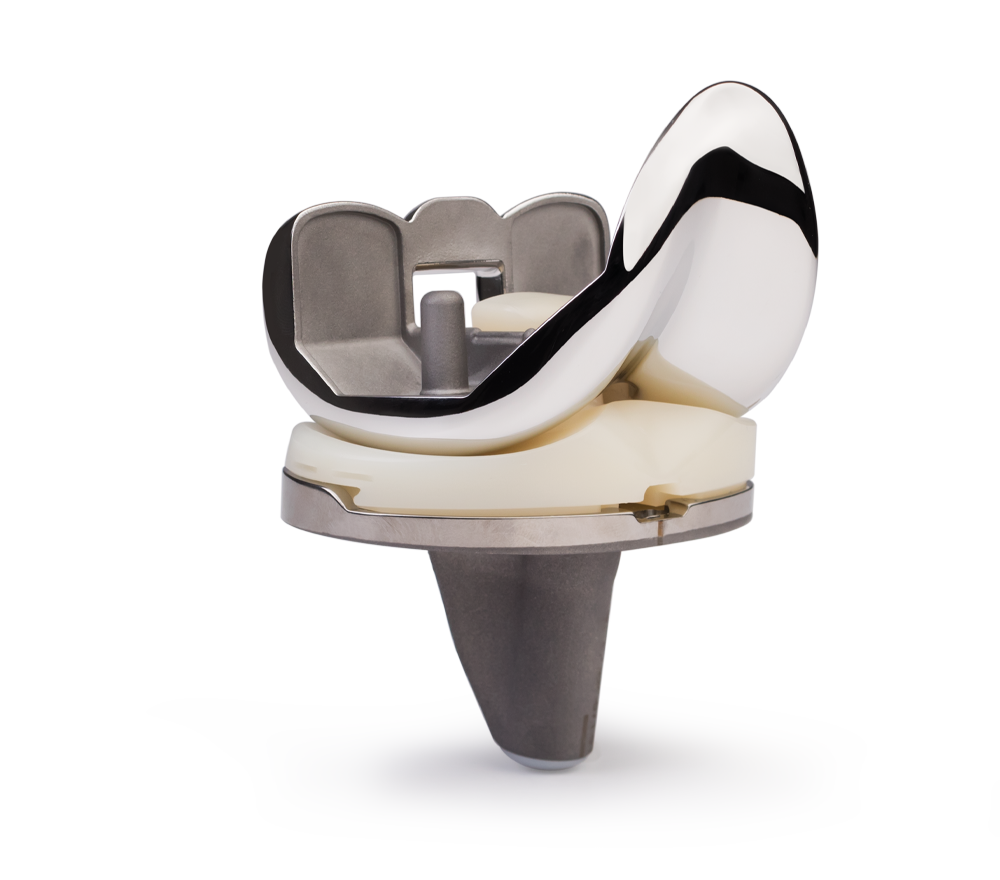
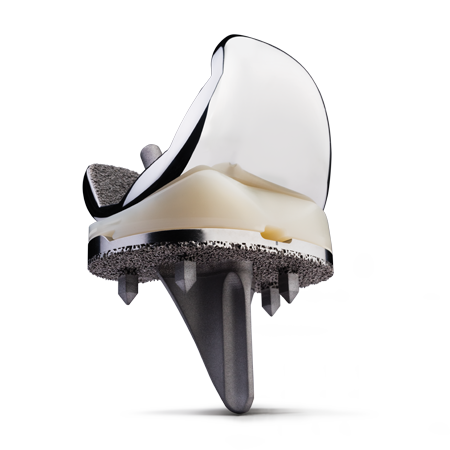
Implants Designed to Improve Outcomes
Technologies are only as good as the implants they are used with. ROSA Knee supports our leading knee brand: Persona® The Personalized Knee®, including the Persona® OsseoTi® Keel Tibia. When it comes to stability, our Persona OsseoTi Anatomic Keel Tibia is more stable with up to 50% less micromotion than a competitor’s symmetric tibia.5*
Accurate
Improve Your Accuracy and Precision
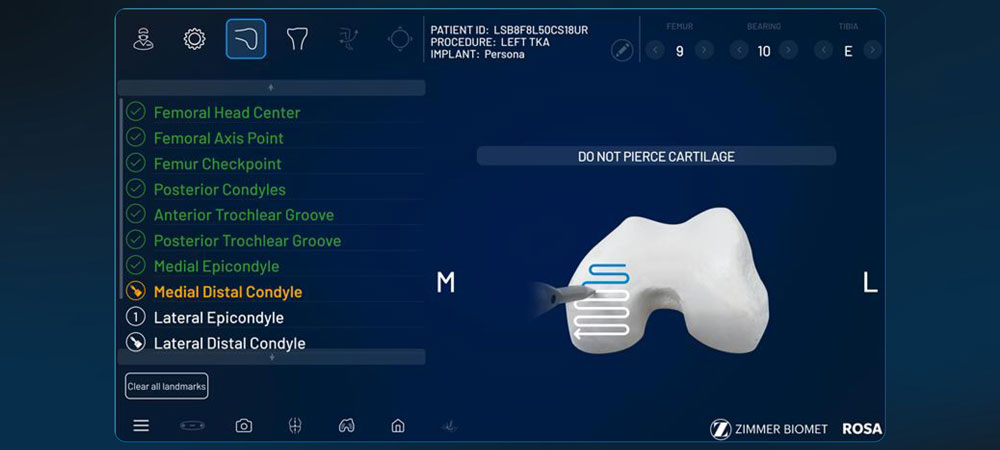
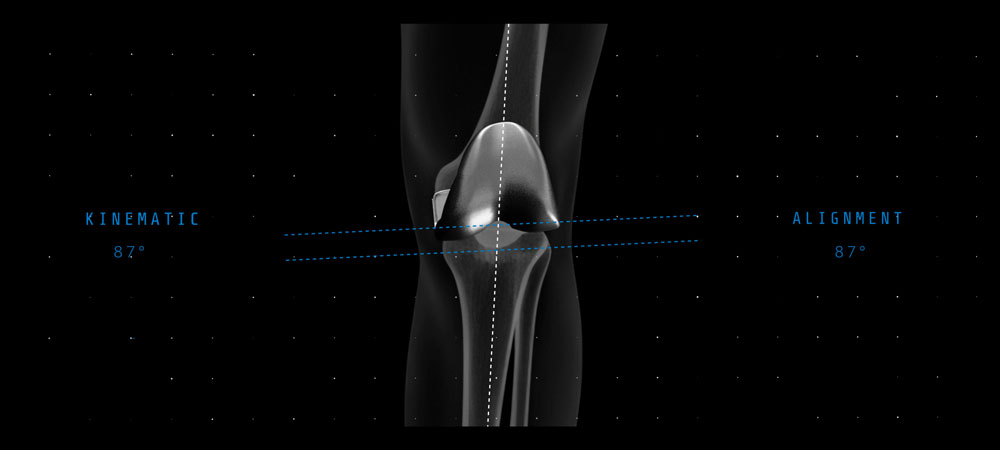
Reduces landmark variability and improves accuracy and precision to your pre-operative plan for optimal implant placement and reproducibility.1
Efficient
Enhance Surgical Efficiency
ROSA Knee has shown a minimal initial learning curve,6 rapid intra-operative assessment of medial and lateral extension gap characteristics and flexible imaging options, including imageless and image-based, enhance efficiency.
Data-Driven7
Making the best decision when it matters requires data-driven intelligence.
Unlock data-driven capabilities for ROSA Knee with ZBEdge® Analytics.
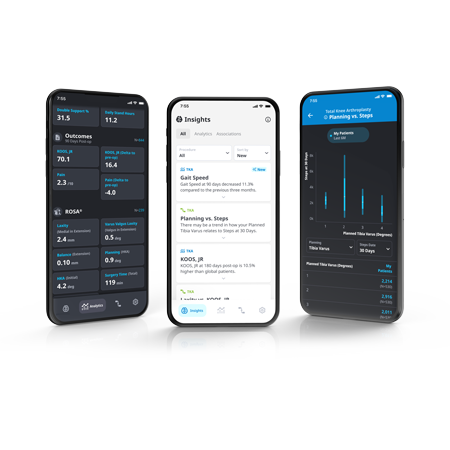
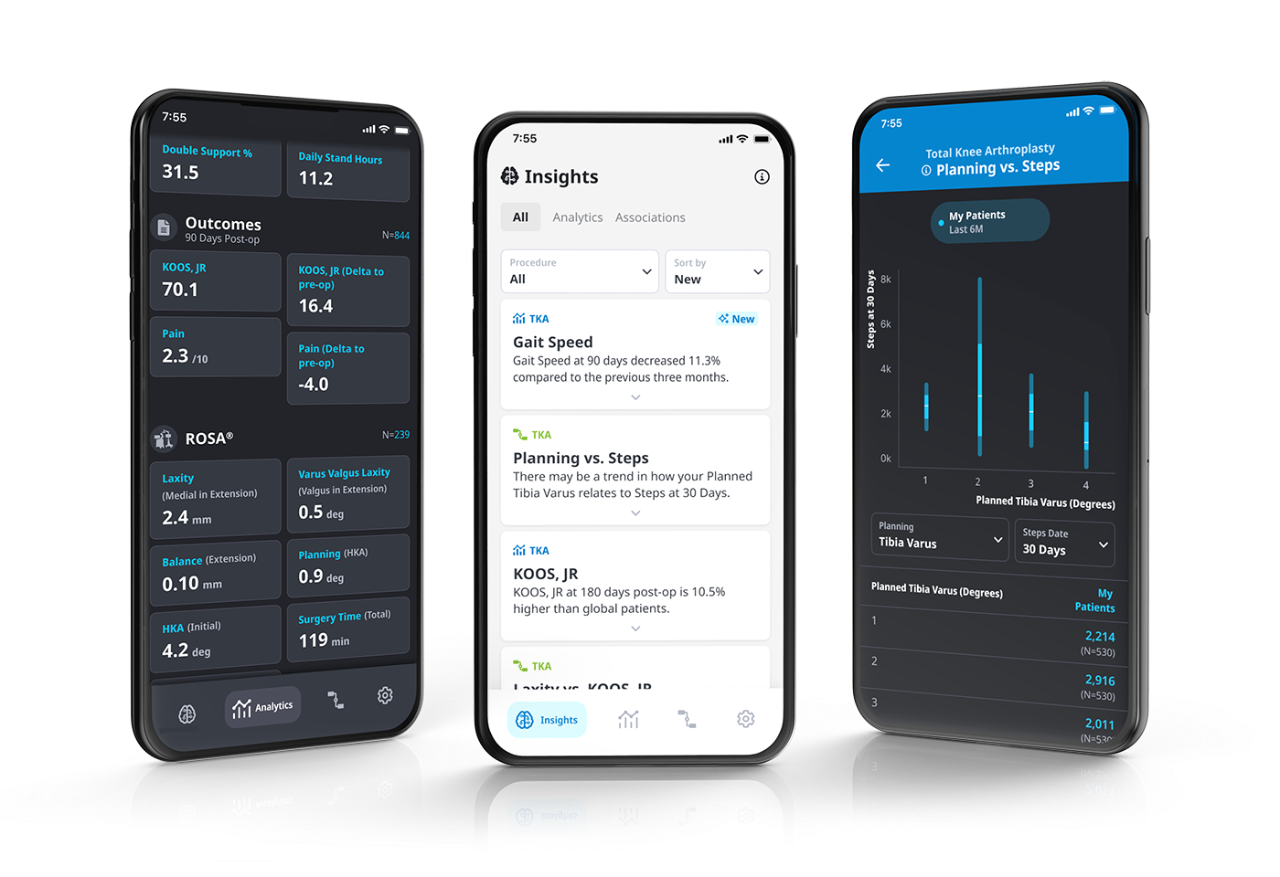
ZBEdge® Analytics
ZBEdge® Analytics is a data platform that delivers intra-operative, mobility and outcome insights accessible directly on a smartphone, enabling surgeons to objectively assess their performance and understand the potential impact of clinical decisions on patient recovery.
- Connect: Analyze and compare the potential impact of surgical decisions on patient recovery using intra-operative data alongside mobility and outcome metrics.
- Understand: Relevant insights delivered in an effortless and actionable format through a personalized data experience.
- Improve: Monitor performance and benchmark progress to identify potential opportunities to improve by uncovering new insights from data.
ROSA MedEd Events
Videos
ROSA® Knee with OptimiZe™ User Experience Video
ROSA® Knee with OptimiZe™ Brand Anthem
ROSA® Knee with OptimiZe™ Surgical Technique Video
Related Products
SUBMIT YOUR INFORMATION AND GET CONTACTED BY A ZIMMER BIOMET REP
Disclaimer
All content herein is protected by copyright, trademarks and other intellectual property rights, as applicable, owned by or licensed to Zimmer Biomet or its affiliates unless otherwise indicated, and must not be redistributed, duplicated or disclosed, in whole or in part, without the express written consent of Zimmer Biomet.
This material is intended for health care professionals. Distribution to any other recipient is prohibited.
For product information, including indications, contraindications, warnings, precautions, potential adverse effects and patient counseling information, see the package insert or contact your local representative; search this website for additional product information. To obtain a copy of the current Instructions for Use (IFU) for full prescribing and risk information, please visit labeling.zimmerbiomet.com or call 1-800-348-2759, press 4 for 411 Technical Support.
For additional robotic inquiries and concerns, contact 1-855 ROSA BOT.