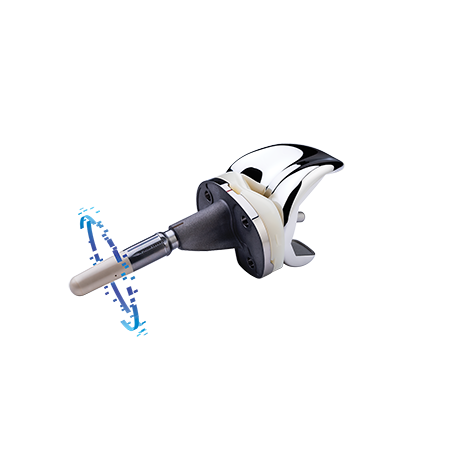
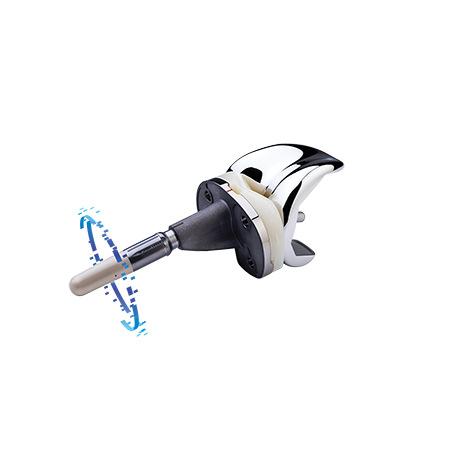
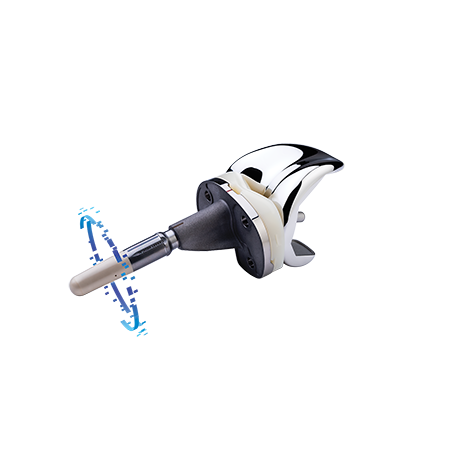
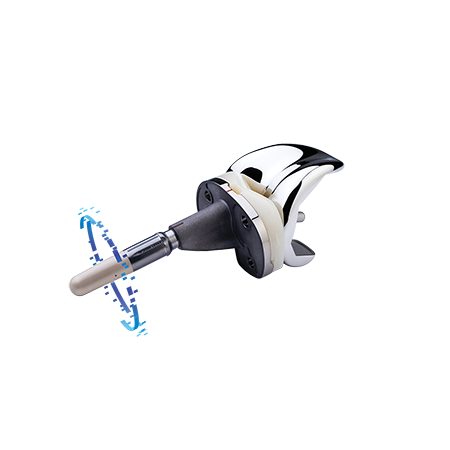
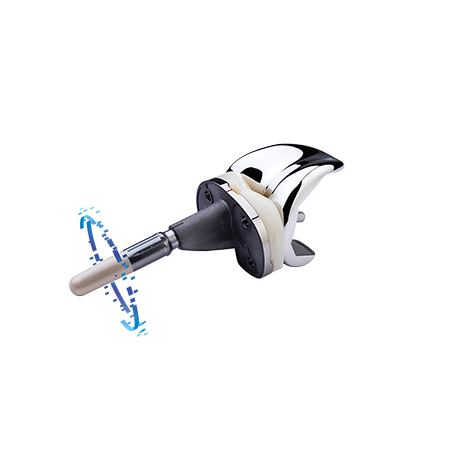
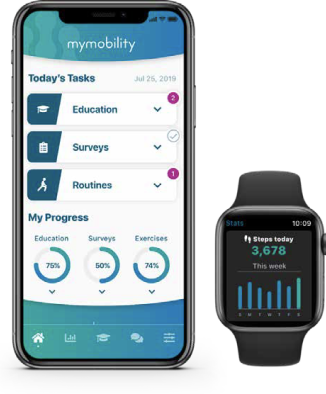
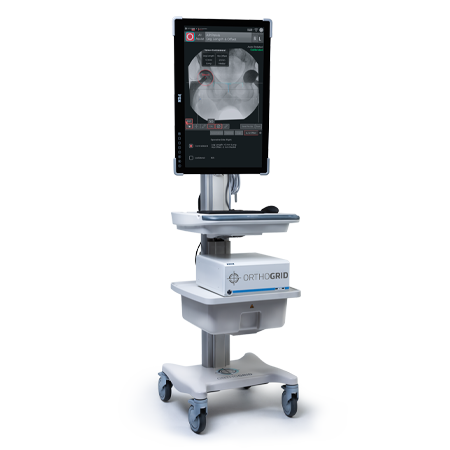
Indications and contraindications can be found here.
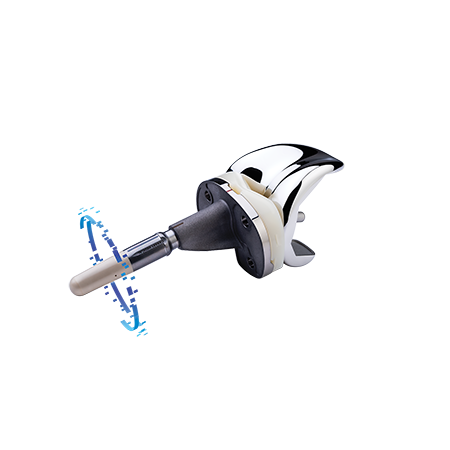
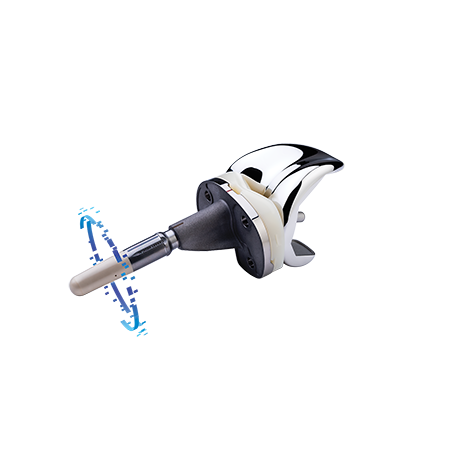
Persona IQ: The objective kinematic data generated by the CTE with CHIRP System are not intended to support clinical decision-making and have not been shown to provide any clinical benefit.
For full prescribing information for the CANARY canturio ™ te, refer to physician instructions for use.
canturio™ Legal Manufacturer
Canary Medical USA LLC
2710 Loker Ave. West
Suite 350
Carlsbad, CA 92010
Customer Service: 1-833-692-2627
canarymedical.com
canturio™ Exclusively Distributed By
Zimmer, Inc.
1800 West Center St.
Warsaw, Indiana 46581-0587 USA
Persona® Knee Legal Manufacturer
Zimmer, Inc.
1800 West Center St.
Warsaw, Indiana 46581-0587 USA